Thursday, November 20, 2008
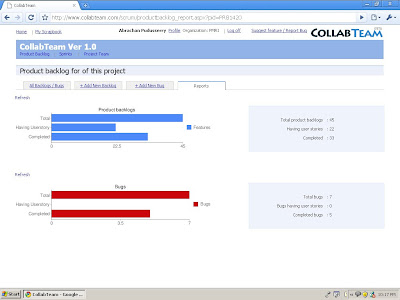
# 9 Monitoring the product backlog entries Vs User stories

Wednesday, November 12, 2008
# 8 Program management using CollabTeam
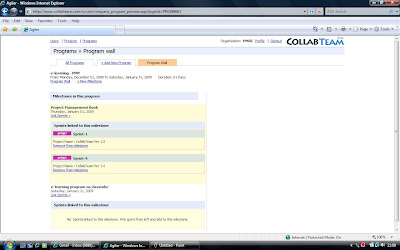 A program is a collection of inter related projects, when done together gives the stakeholders some added advantages, than doing them one after the other (thanks to PMBOK). Consider a situation, where multiple project teams operating from different geographies contributing to a program (or position yourself as a super product owner, who has multiple project teams contributing tp your program). CollabTeam provides you with the following features to cater to this situation in a seamless fashion.
A program is a collection of inter related projects, when done together gives the stakeholders some added advantages, than doing them one after the other (thanks to PMBOK). Consider a situation, where multiple project teams operating from different geographies contributing to a program (or position yourself as a super product owner, who has multiple project teams contributing tp your program). CollabTeam provides you with the following features to cater to this situation in a seamless fashion.- A program comprising of multiple milestones (road map) can be defined using the program option under the administrator module (log in as administrator).
- Sprints under the projects within the company can be linked to the milestones
This feature helps to integrate the outputs of multiple sprints across projects to a milestone at the program level.
# 7 Handling of defects by collabteam
Wednesday, November 5, 2008
# 6 Sprint Velocity
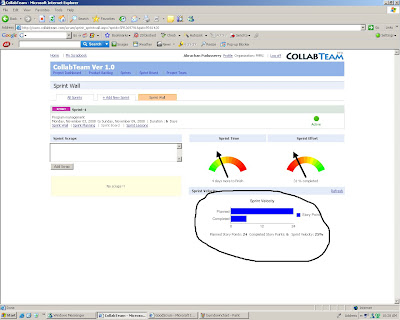 Sprint velocity calculations help the team to learn and continuously improve.
Sprint velocity calculations help the team to learn and continuously improve.Sprint velocity = (work units completed / work units committed) during the sprint * 100
During the initial sprints, it is quite likely that teams can fail becuase they either over committed work or under committed. In the former case, at the end of the sprint, the team might not have completed the work committed at the start of the sprint. In the latter case, the sprint will get over before the sprint end date. After some learning through a couple of sprints, the team will learn to complete what they committed within the stipulated time frame. At that time, the sprint velocity calculation will show 100%.
# 5 Sprint Burn down chart
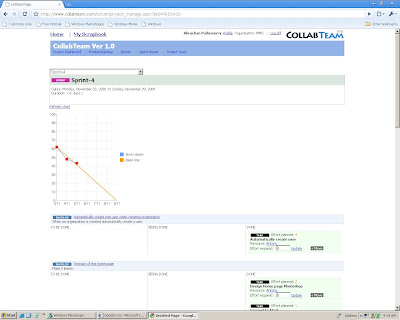
isions as the sprint progresses. The 'Y' axis shows the 'effort' required to complete the balance work in tyhe sprint and the 'x' axis, the number of days of the sprint. The objective is to make the effort required to complete the sprint zero on or before the sprint end date.
In the conventional project management, we use the earned value management. The earned value chart focuses on the work completed so far. In the case of a burn down chart, the focus is on balance effort required to complete the pending activities.
Collabteam feature
Collabteam has the sprint burn down feature. The burn down is derived from the 'balance effort' against the tasks, which the team members updates regularly.
# 4 Sprint Board
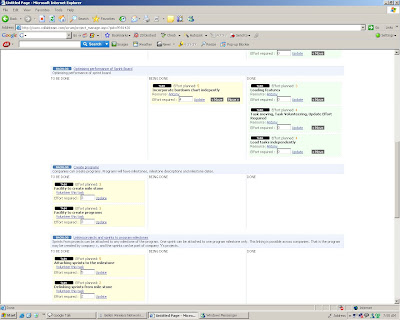
are requested to volunteer the work. Once the work gets volunteered it moves on to the 'being done' column and finally when it gets done, it moves to the 'done' column. Work volunteering is an integral part of scrum. Work volunteering brings in more ownership and pride in work.
When the tasks are progressing, the team members can update the effort required to complete the remaining part of the work on a daily basis. This helps to forecast the total effort required to complete the balance activities in the sprint
# 3 Sprint backlog
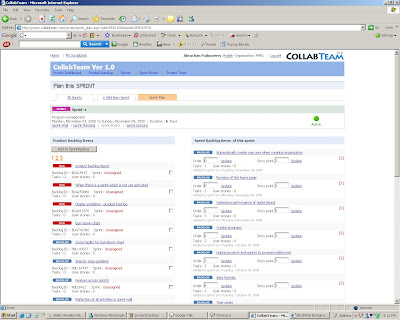
Tuesday, November 4, 2008
# 2 Product backlog

- Product backlog is owned by the product owner
- It is the wish list of the features to be developed
- During the sprint planning meeting, a subset of the features from the product backlog is taken up for production.
- Before taken up for production, the product backlog entries are elaborated into user stories
- A user story contains a narration of the feature to be developed, the accetance test cases for that feature.
- All clarifications that happens during the feature development are captured as conversations in the product backlog.
- The product backlog entry and the user story provides sufficient information for the tem members to estimate and develop the features. This replaces the conventional software requirements specification.
- CollabTube has the feature to create the product backlog, assign estimates, categorize them into high, medium, low priority.
- Against every product backlog entry, user stories can be created. User story comprises of a small narration of the feature to be developed, acceptance tests, and conversations ( all the discussions that happen during development regarding the feature).
# 1 What is scrum?

- SCRUM is one of the project management methodologies of the agile family
- It is simple and light weight
- Of the constraints of time, cost and scope, time is the only one "non-negotiable'
- Based on self organized teams and a servant leader (scrum master)
- Scrum is based on the agile manifesto
- Scrum team values everything that adds value to the project's deliverables, (that means, they are against everything which does not add any value to the project's deliverable.
- SCRUM is based on the value systems of commitment, focus, openness, respect and courage.
- SCRUM is based on meritocracy (protecting the strong)
- The key building blocks of scrum framework are product backlog, sprint planning meeting, sprint backlog, sprints, daily scrums, demo meetings and lessons learned at the end of every sprint.
- The key roles in the scrum team are product owner (the custodian of product backlog and featuriritization), the scrum master (implementing scrum within the teams and removing impediments to the team) and the team members.
- There are no specific titles for the team members. team members are selected based on their core competencies (some based on their coding skills, some others for their testing skills, some others for domain knowledge) and at the same time anybody can volunteer for any pending activity.
- There is no concept of work allocation in scrum teams. Work is displayed and the team members can volunteer.
- At the beginning of a sprint, the product owner, scrum master and the team decides / agrees on the features to be developed during the sprint. This is done through a sprint planning meeting (8 hour meeting for a 30 day sprint - Our sprints are 6 day sprints hence the sprint planning time is much lesser). The sprint durations are identical (cannot have one sprint of 10 days, then a 20 day sprint followed by another 30 day sprint).
- During the sprint planning meeting, the time and venue of the demo meeting (at the end of the sprint), the participants and the acceptance test are also finalized.
- During the sprint, the team works on the agreed upon features.
- Every day the team has a scrum meeting (daily stand up meeting). During the meeting every team member reports the status of her work to the rest of the team.
- In case the team members need some help to remove impediments, they are also highlighted during the scrum meeting (resolved by the scrum master).
- Upon completion of the sprint, the team demonstrates the features developed to the demo meeting participants.
- At the end of every sprint, a lessons learned exercise is conducted (to be addressed before the start of the next sprint).
- The team gets into the planning of the next sprint


